Cooling Tower Theory
Cooling Tower: Understanding Its Function, Types, and Benefits
A Cooling Tower is an essential component in industrial cooling systems, playing a crucial role in dissipating excess heat from processes such as power generation, HVAC systems, and manufacturing industries. By utilizing the principles of heat exchange, a Cooling Tower cools down water and enhances energy efficiency in various applications.
Cooling Towers are classified into two main types based on how air circulates through the system:
1. Natural Draft Cooling Tower
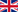
A Natural Draft Cooling Tower relies on the natural movement of air to facilitate cooling. When heated, air rises naturally, creating a draft that draws in cooler air to replace it, leading to effective heat dissipation.
- Advantages: No mechanical fans required, making it energy-efficient.
- Disadvantages: Efficiency depends on external environmental factors such as wind speed and temperature.
- Applications: Typically used in large-scale industrial operations, such as power plants and chemical processing plants, where extensive heat dissipation is required. See Figure 1
2. Mechanical Draft Cooling Tower
A Mechanical Draft Cooling Tower utilizes fans or blowers to enhance airflow, resulting in improved cooling performance. It can be further categorized into two main types:
2.1 Forced Draft Cooling Tower
- The fan is positioned at the air intake section to force air into the tower.
- Advantages: Provides controlled airflow and high-pressure air circulation.
- Disadvantages: Requires additional power consumption for fan operation.
- Best suited for: Environments requiring precise air movement control. See Figure 2
2.2 Induced Draft Cooling Tower
- The fan is placed at the air outlet to pull air through the system.
- Advantages: More efficient at preventing heat recirculation compared to forced draft systems.
- Best suited for: Various industrial applications due to its superior performance. See Figure 3
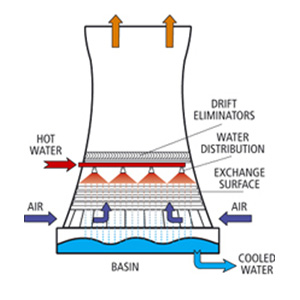
Figure 1
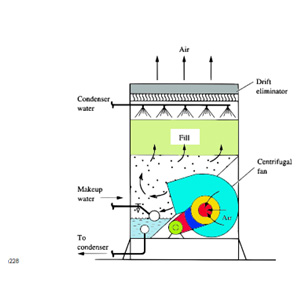
Figure 2
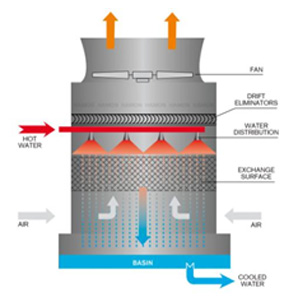
Figure 3
Cooling Tower Types Based on Heat Exchange Mechanism
In addition to airflow classification, Cooling Towers can be further categorized based on how air and water interact within the system:
1 Crossflow Cooling Tower
- Water flows vertically through a filler (heat exchange media), while air flows horizontally across it.
- Advantages: Lower air resistance, requiring less fan energy consumption.
- Disadvantages: Slightly lower cooling efficiency compared to counterflow systems.
- Applications: Ideal for moderate heat dissipation requirements in industries such as food processing and manufacturing. See Figure 4
2 Counterflow Cooling Tower
- Water flows downward, while air moves in the opposite (counterflow) direction, maximizing the cooling effect.
- Advantages: Higher cooling efficiency due to prolonged contact between air and water.
- Disadvantages: Higher air resistance, requiring more fan power.
- Applications: Best suited for high-performance cooling applications such as chemical plants, data centers, and heavy industries. See Figure 5
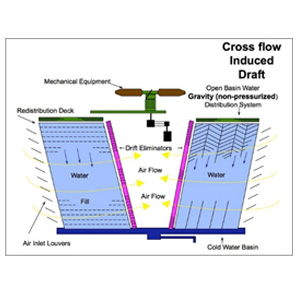
Figure 4
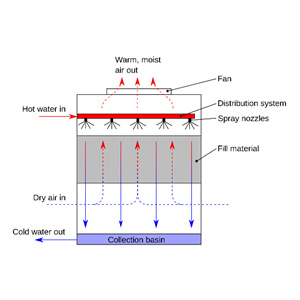
Figure 5
✅ Energy Efficiency – Selecting the optimal Cooling Tower reduces power consumption and operational costs.
✅ High Cooling Performance – Effectively lowers water temperature for enhanced process efficiency.
✅ Versatile Applications – Used in HVAC systems, power plants, food manufacturing, and petrochemical industries.
✅ Eco-Friendly Solution – Minimizes carbon footprint and optimizes water usage for sustainable cooling.
✅ High Cooling Performance – Effectively lowers water temperature for enhanced process efficiency.
✅ Versatile Applications – Used in HVAC systems, power plants, food manufacturing, and petrochemical industries.
✅ Eco-Friendly Solution – Minimizes carbon footprint and optimizes water usage for sustainable cooling.
Conclusion
Choosing the right Cooling Tower is critical to optimizing industrial cooling efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and ensuring long-term operational success. Whether you require a Natural Draft Cooling Tower for large-scale power generation or a Mechanical Draft Cooling Tower for precise temperature control in industrial processes, selecting the best cooling system will ensure maximum performance and cost-effectiveness.
For more information on Cooling Towers and how to integrate them into your operations, consult our experts today!
Preventive Maintenance
| Spare Parts | Description |
| Fan Blade & Hub | →Check if any nuts loosened out →Check fan blade condition if any crack, bend or twist |
| Gear Reducer | →Check if any abnormal noise →Check if any oil leak at drive shaft, motor flange or gear housing →Check oil level and see if any water content |
| Filler | →Clean with high pressure water jet if dirty |
| Water Basin | →Clean with plastice brush if moss or algae found |
| Tower Wall | →Clean with plastice brush both inside and outside if found dirty |
| Tower Structure | →Structure is made of hot dip galvanized steel, it can rust after some time. Regular check may required. If rust found, it should be cleaned and repainted. Check also bolts and nuts. Replace them if rusted. |